The human body is a perfect machine, in this wonderful article we will try to clarify why women need to train entertainingly from men.
Remember, there is no pretentious will to favor one “sex” over the other 🙂 Simply women and men are deeply different, much more than you think.
This is a very important thing to understand, so you can use this information during sports programming of athletes.
Are you ready? Let’s start then!
Indice dei contenuti
1. Women should have a high fat diet
Does that sound strong? But let us explain it better.
Women burn more fat, less carbohydrates and less protein than men at the same intensity of exercise. Since they rely less on carbohydrates as fuel, they do not store as much glycogen during carbohydrate refills.
Both differences in the nervous system and hormonal system, including estrogen, are responsible for women’s reduced dependence on glycogen.
For example, adrenaline, the hormone of struggle or flight, burns more fat in women than men .
A more obvious explanation is that women normally have a considerably higher fat percentage than men of the same weight , not only on the body but also within the muscles, so it makes sense to use it as a primary energy source.
Basically, women have a glycogen and protein-sparing metabolism. This means that women don’t need as many carbohydrates or proteins in their diet as men to power their exercise sessions.
The lower carbohydrate requirement frees up calories to be consumed in the form of fat. Fats have very positive effects on the hormonal and cardiovascular health of women. In general, the more fat women eat, the more estrogen and testosterone they produce . Testosterone and estrogen are both anabolic hormones, despite the broscience that is often overheard about estrogen.
Low fat diets can also reduce breast size, in part probably due to low production of sex hormones, since estradiol and IGF-levels1 are significantly related to breast size in women who do not take the birth control pill.
A high fat diet can also be easier for women to follow than men. Dietary fats are 15% more satiating in women than men.
Women also have less to fear from the potential negative effects of a low-carb, high-fat diet.
Fats do not decrease insulin sensitivity in both women and men. Estrogen plays an important role. It helps to control inflammation, burn fat and preserve insulin sensitivity. Less inflammation means that polyunsaturated fats in particular are less susceptible to oxidation, so they can exert their anabolic effects.
Women generally have much better metabolic health than men and have a healthier body fat distribution.
By the way, if you are concerned about breast cancer, the relationship between fat intake and breast cancer risk lies in poor epidemiological studies of inactive and overweight women eating processed junk fat, such as processed red meat.
Back on the subject, several studies have found that women with polycystic ovary syndrome lose more fat and less muscle with a low-carbohydrate diet than a low-fat diet , even when protein and energy intake is strictly controlled.
Several studies have found similar results in overweight and healthy women, but these studies have been confused by more protein in low carbohydrate diets. In fact women with more fat in their diet burn more calories during exercise, have more strength and are leaner.
The benefits of fat compared to carbohydrates depend on the woman’s carbohydrate tolerance. However, we can safely say that the popular diets very rich in carbohydrates and almost zero fat are not optimal for most women.
Finally, women do not need as much protein as men for various reasons.
-
- Women oxidize less protein during exercise than men.
- Women also burn less protein on a fast or after meals than men.
- Because of their increased essential fat mass, women generally have less lean body mass than men of the same weight.
</ol
A meta-analysis found that women’s protein needs are almost exactly 10% lower than men’s. In fact, from an evolutionary point of view, women may have adapted better than men to a lower protein intake.
2. Women have more results with higher repetitions
Untrained men and women have the same distribution of fiber type.
In strength training women, muscle fibers are converted into type I fibers or do not convert at all, while in men they generally change to type IIa fibers.
Women also have type I fibers proportionally larger than men.
The result of this and other mechanisms is that women are more resistant to fatigue than men , even when comparing women and men with the same level of strength.
Women can generally do more repetitions at a certain intensity than men. So, to train to a certain target workout intensity, women should generally perform more repetitions per set than men.
3. Women can handle more volume
Having larger and type I fibers allows women to manage more volume than men.
Thanks to estrogen which is an anticatabolic hormone that helps in muscle repair, reduces protein degradation during exercise and protects against muscle damage.
This allows women to train with a higher training volume without going into overtraining. Women can therefore tolerate training stress better than men.
4. Women should do less explosive training
Women’s superior working ability disappears when they train with weights close to their maximum strength (1RM) . While women’s muscles have great endurance, the female nervous system is not as efficient as that of men.
Men are more explosive than women: they can generate strength faster. The area of the brain that controls movement (the motor cortex) is in fact literally larger in men, even after correcting the height.
During explosive exercise at very high training intensities, such as powerlifting, men can perform more repetitions than women.
A more efficient motor cortex is why men tend to do better in explosive sports. However, the difference becomes very small after intensive training.
Sports scientist Renato Manno and his team compared the strength and explosiveness of 900 elite male and female athletes in 30 sports in a research and found that compared to body weight, women were as strong as men and only a small percentage less explosive.
This makes sense since women have the same relative natural muscle potential as men. The sociocultural differences probably explain why we no longer see women in high-level athletics.
Men are most powerful only during explosive and dynamic contractions, not during heavy negative or isometric contractions, even at high intensity.
So it is not true that women should never train heavily. However, women should train their strengths.
Explosive exercise does not allow women to train with the same volume as men. Women also recover less well after explosive exercises such as sprints. In contrast to the generally greater resilience of women, high-volume sprint training can take over 72 hours to recover in women.
This results in worse training adaptations for explosive exercise in women. For example, women do not build as much muscle protein after high-intensity sprints as men.
This is actually amazing, because after regular strength training, women build the same amount of muscle protein as men.
5. Women respond better to stationary cardio than HIIT
Since women do not react equally well to high-intensity interval training, stationary cardio works best for them. And not only physically: mood improvements due to aerobic exercise tend to be greater in women than in men.
6. Women do better with a slower lifting rate
Because women are less explosive than men, women can perform more repetitions with a more controlled and less explosive lifting rhythm. Forcing women to use a fixed and fast pace does not take advantage of their increased resistance.
7. Women tolerate metabolic stress better
Another reason why women have better stamina than men is that women suffer less metabolic stress than men, even when comparing women and men of the same strength level.
Women have lower blood pressure during exercise, so they can get more blood and oxygen to the muscles than men. Less metabolic by-products accumulate in the blood, so the muscles are able to function longer under stress than men.
According to some research, the superior fatigue resistance of women disappears during training due to the occlusion of blood flow (KAATSU, as the Japanese inventors originally called it).
And unlike men, women’s muscle growth seems to be blocked by occlusion of post-exercise blood flow.
8. Women do not need so much rest between the series
The following graph of Dr. Hunter extrapolated from this splendid research summarizes the reasons why women don’t work as hard as men. Women do not need as much rest as men to complete the same relative training volume.
women suffer less fatigue than men
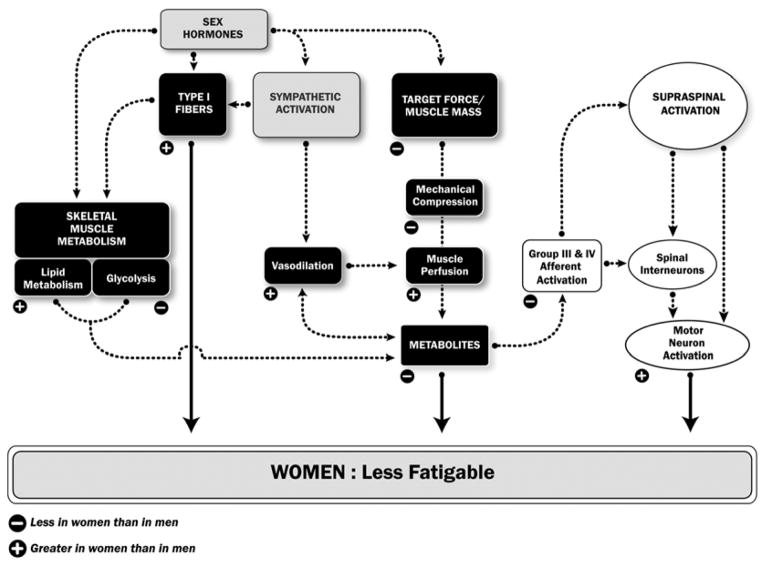
9. Women can train with a higher training frequency
Women not only recover faster after a set. They also recover faster after a training session. This, too, should not be a surprise now, since women have a better supply of nutrients to their muscles, do not suffer so much muscle damage and repair their muscles faster.
Conclusion
Most women are intuitively aware of their strengths in the gym, but they are often told to train exactly like men.
As a result, they may not realize their athletic potential.
Males often instinctively perform high-intensity workouts with long resting intervals, explosive repeat cadences, and HIIT-style cardio.
Women are naturally much more inclined to do cardio in steady state, lift with a more controlled rhythm, perform higher repetitions, take shorter rest periods and do a more total job.
Basically, women and men benefit from the same programming principles, but these gender differences can allow women to optimize their rate of progression.
Through millions of years of evolution, women have adapted better to workouts that are closer to the resistance spectrum than men.
Women’s gym
Finally, we are writing an article about the benefits of the women’s gym that we’ve been writing lately. A very useful and easy to read article. You can find it here</a
Sources
Sex Differences in Human Fatigability: Mechanisms and Insight to Physiological Responses
Post-exercise blood flow restriction attenuates muscle hypertrophy
Sex differences in muscle fatigability and activation patterns of the human quadriceps femoris







